Home ⇒ Tooth Whitening
Tooth whitening has become a popular cosmetic dental procedure, offering individuals the opportunity to enhance the brightness of their smiles. This comprehensive guide explores the various methods of tooth whitening, the procedure involved, potential risks, and aftercare practices.
Extrinsic Stains: External factors such as food, beverages, tobacco, and poor oral hygiene can lead to surface stains on the enamel.
Intrinsic Stains: Discoloration originating from within the tooth, often due to aging, certain medications, or dental trauma, is referred to as intrinsic stains.
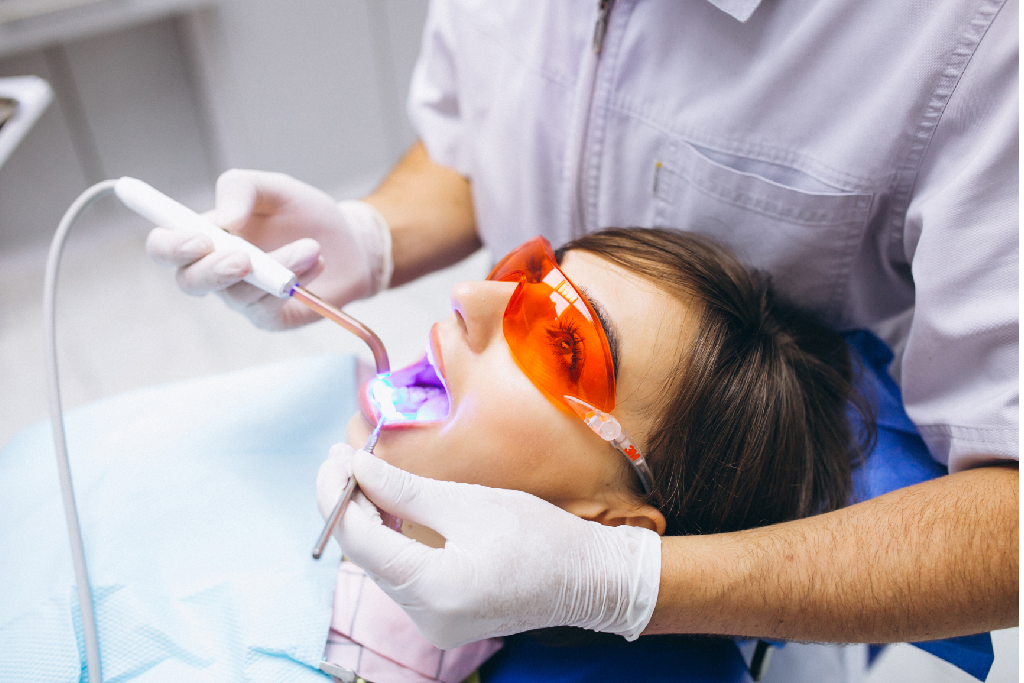
In-Office Professional Whitening: Conducted by a dentist, in-office whitening involves the application of a high-concentration peroxide gel on the teeth, often activated by a specialized light. This method provides immediate and noticeable results.
Take-Home Whitening Kits: Dentists may provide custom-fitted trays and a lower-concentration whitening gel for at-home use. This method allows individuals to achieve a gradual whitening effect over a specified period.
Over-the-Counter Whitening Products: Commercially available whitening toothpaste, strips, and gels typically contain lower concentrations of bleaching agents and may offer modest results with consistent use.
In-Office Professional Whitening: Conducted by a dentist, in-office whitening involves the application of a high-concentration peroxide gel on the teeth, often activated by a specialized light. This method provides immediate and noticeable results.
Take-Home Whitening Kits: Dentists may provide custom-fitted trays and a lower-concentration whitening gel for at-home use. This method allows individuals to achieve a gradual whitening effect over a specified period.
Over-the-Counter Whitening Products: Commercially available whitening toothpaste, strips, and gels typically contain lower concentrations of bleaching agents and may offer modest results with consistent use.
Copyright © 2023 sarita sublok dental All Right Reserved. Designed by 